Anat Pardo(1,2), Shiri Barbash-Hazan(1,2), Anat Shmueli(1,2), Michal Eisner(1,2), Sharon Sigal(1,2), Arnon Wiznitzer(1,2), Asnat Walfisch(1,3), Tomer Sela(4), Leor Wolff(4), Eran Hadar(1,2)
- Helen Schneider Hospital for Women, Rabin Medical Center, Petah-Tikva, Israel
- Faculty of Medical and Health Sciences, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel
- Dina Recanati School of Medicine, Reichman University, Herzliya, Israel
- Translational Innovation and eHealth wing, Clalit Health Services, Tel-Aviv, Israel
OBJECTIVE
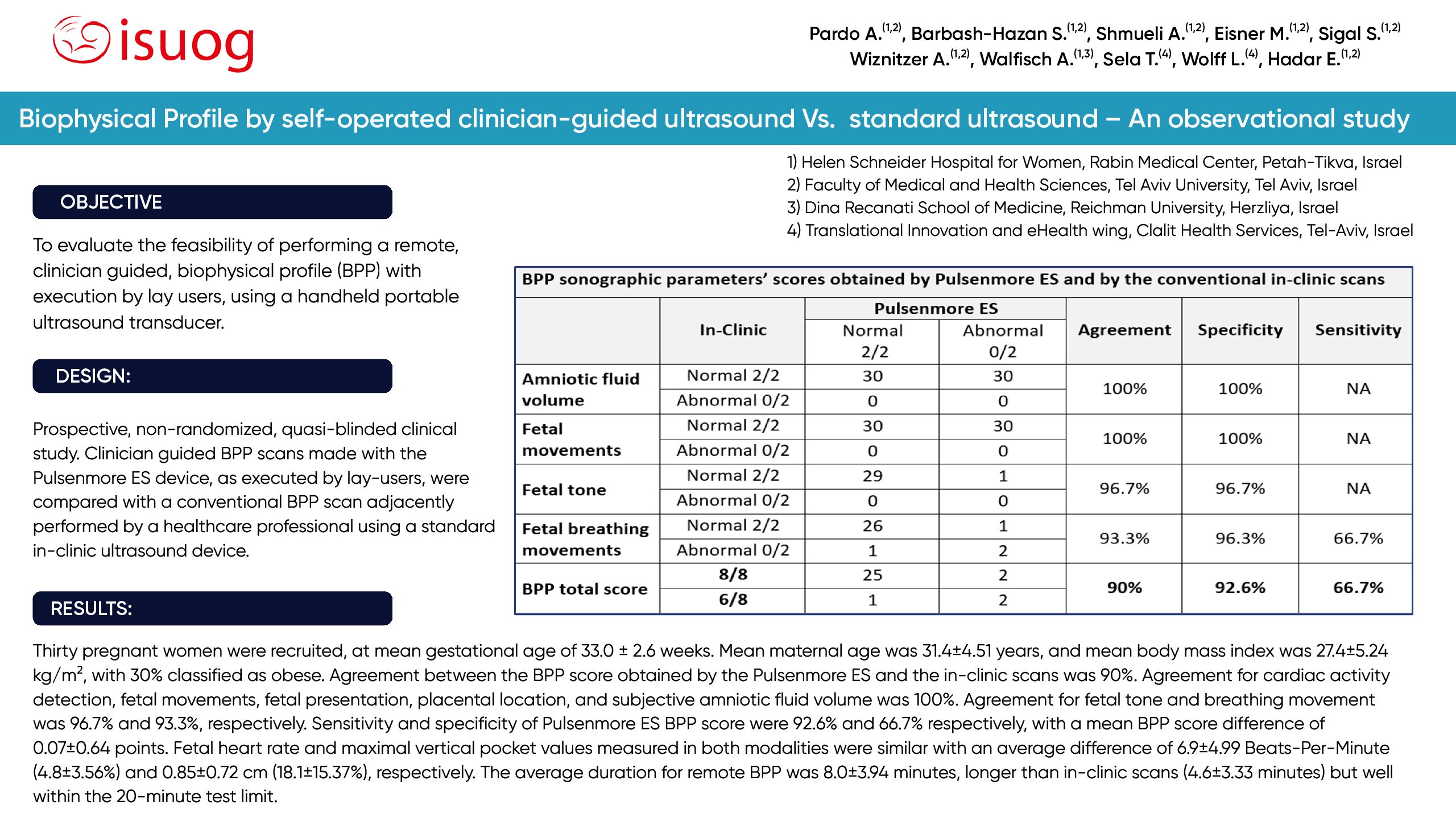
To evaluate the feasibility of performing a remote, clinician guided, biophysical profile (BPP) with execution by lay users, using a handheld portable ultrasound transducer.
DESIGN
Prospective, non-randomized, quasi-blinded clinical study. Clinician guided BPP scans made with the Pulsenmore ES device, as executed by lay-users, were compared with a conventional BPP scan adjacently performed by a healthcare professional using a standard in-clinic ultrasound device.
RESULTS
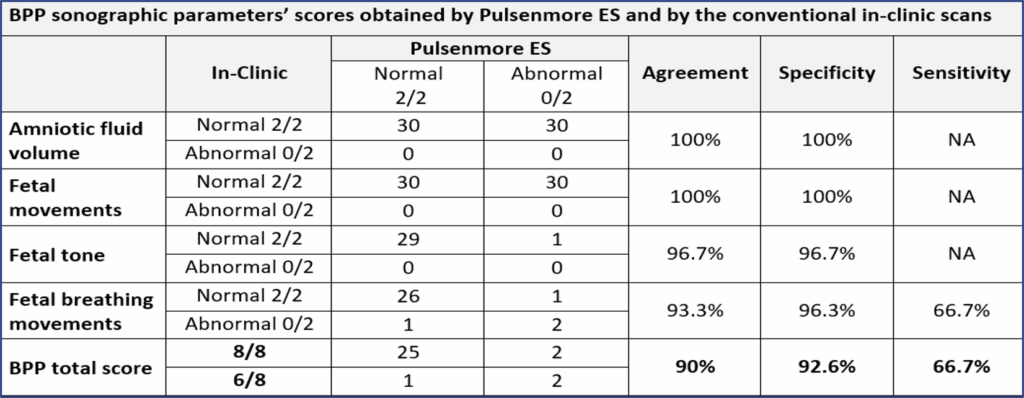
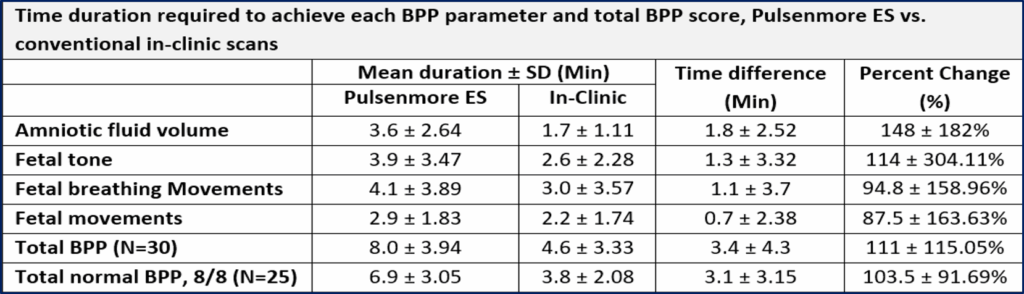
Thirty pregnant women were recruited, at mean gestational age of 33.0 ± 2.6 weeks. Mean maternal age was 31.4±4.51 years, and mean body mass index was 27.4±5.24 kg/m², with 30% classified as obese. Agreement between the BPP score obtained by the Pulsenmore ES and the in-clinic scans was 90%. Agreement for cardiac activity detection, fetal movements, fetal presentation, placental location, and subjective amniotic fluid volume was 100%. Agreement for fetal tone and breathing movement was 96.7% and 93.3%, respectively. Sensitivity and specificity of Pulsenmore ES BPP score were 92.6% and 66.7% respectively, with a mean BPP score difference of 0.07±0.64 points. Fetal heart rate and maximal vertical pocket values measured in both modalities were similar with an average difference of 6.9±4.99 Beats-Per-Minute (4.8±3.56%) and 0.85±0.72 cm (18.1±15.37%), respectively. The average duration for remote BPP was 8.0±3.94 minutes, longer than in-clinic scans (4.6±3.33 minutes) but well within the 20-minute test limit.
CONCLUSIONS
BPP, obtained by the Pulsenmore ES ultrasound device, operated by lay users, during synchronized telehealth guidance, demonstrates high accuracy and reliability for clinical use compared to standard BPP.