Authors:
S.S. Njonou Noujiep, W. Henrich
Affliation:
Department of Obstetrics, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
https://doi.org/10.1002/uog.28018
Objective:
According to literature, over 40% of women give birth after the estimated date of delivery (EDD). Management ranges from monitoring to intervention. Telemedicine is evolving and increasingly, self-operated portable devices are being used. In this study, we examined the INSTINCT device for fetal assessment in women past the EDD. Our aim was to evaluate whether the patient self-operated scans correlate with the routine scan. Secondly, we aimed to assess whether the mobile-based ultrasound system leads to a reduction in outpatient visits.
Methods:
In this prospective, observational trial, women included had a singleton fetus, and were at least at 40 + 0 gestational weeks. Each woman performed a set of scans with her device. An experienced sonographer performed the routine scans. The patients’ scans were tested for fetal heart activity, amniotic fluid volume, and fetal body movements. They were classified, as normal if all parameters were in the reference range, abnormal if one or more parameters were out of the range or inadequate if, one or more parameters could not be evaluated. The women completed a questionnaire as well to evaluate satisfaction, safety and the question of reduction of outpatient visits.
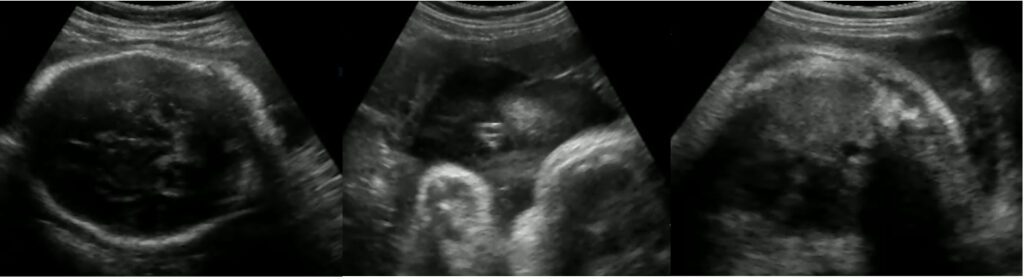
Figure 1: Images showing fetal head, amniotic fluid and fetal heart.
Results
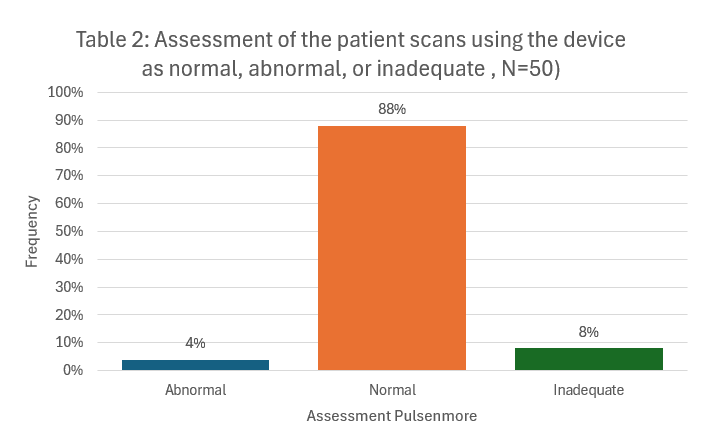
50 women between 40 + 0 and 41 + 2 gestational weeks were included. 88% of the patients’ scans were normal, 4% were abnormal and 8% were inadequate. 91,9% of the patients felt safe using the ultrasound device. 97,9% indicated that they would use such a device during pregnancy and in 81,6%, this would lead to a reduction of doctor’s consultations. The overall satisfaction with the device 4, 65/5.
Conclusions
The INSTINCT ultrasound system is a viable solution for remote fetal assessment and could potentially lead to a cost and time alleviation. There is need for integration of Doppler-mode to the device and for further studies with remote use.


